Click here to download this symptoms card.
It’s important to look for a combination of the warning signs of sepsis. Spotting these symptoms early could prevent the body from entering septic shock, and could save a life.
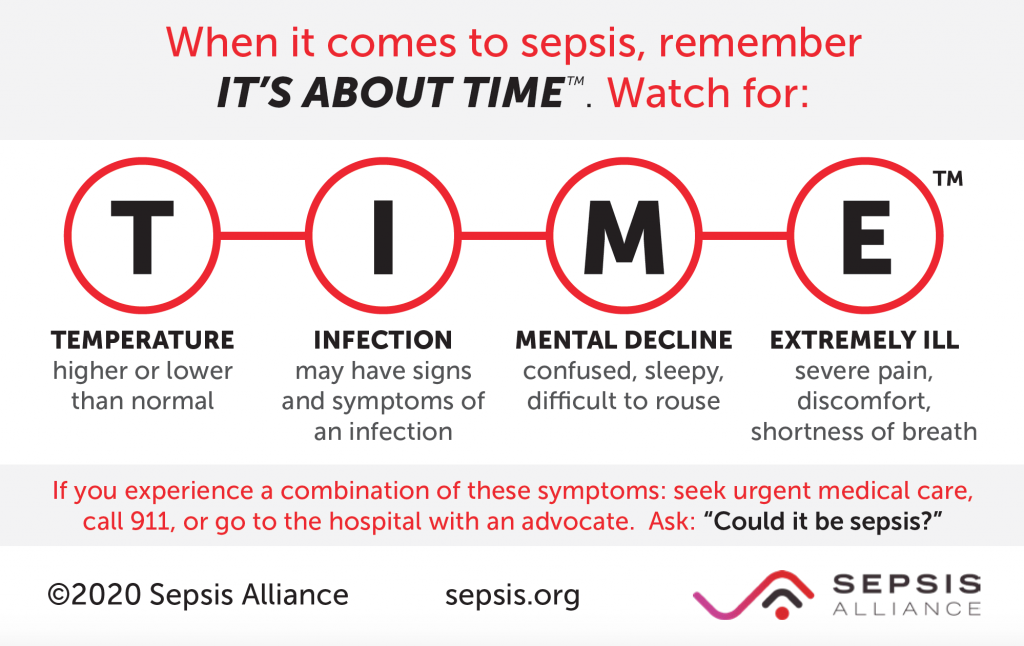
T – Temperature higher or lower.
Your body’s temperature should stay fairly constant, around 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (37 degrees Celsius), moving up or down a bit depending on your activity, the environment, and time of day. A temperature of 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.7 degrees Celsius) is considered to be hyperthermia, a fever. When you have an infection, your body’s temperature usually rises as it tries to fight off the bug causing the infection. Interestingly, some people see their body temperature go down (hypothermia) instead of up. This is why any change, high or low, can be a sign of sepsis.
I – Infection – may have signs and symptoms of an infection.
If you have a local infection, like a urinary tract infection, pneumonia, or an infected cut, the signs and symptoms are localized according to the area affected (needing to urinate or burning on urination for a UTI, coughing and chest pain for pneumonia, redness and pus for an infected cut, for example). If the infection has spread or you have a generalized infection, you may develop other signs and symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, pain, etc.
Sometimes however, you may have an infection and not know it, and not have any symptoms. Keep this in mind especially if you have recently had surgery or an invasive medical procedure, a break in your skin, or you have been exposed to someone who is ill.
M – Mental decline – confused, sleepy, difficult to rouse.
Sepsis can affect your mental status. Some people, especially the elderly, may not show typical signs of infection. Instead, they may show a sudden change in mental status, becoming confused, or a worsening of dementia and confusion. Sleepiness, often severe, is also a common complaint.
E – Extremely ill – severe pain or discomfort, shortness of breath.
Many sepsis survivors have said that when they were ill, it was the worst they ever felt. It was the worst sore throat, worst abdominal pain, or they felt that they were going to die.
Children developing sepsis may exhibit different symptoms, as seen below.

Healthcare professionals look for the following signs and symptoms, as well as those listed above, to determine a diagnosis. They include:
Inflammatory
- High white blood cell count
- Immature white blood cells in the circulation
- Elevated plasma C-reactive protein
- Elevated procalcitonin (PCT)
Hemodynamic
- Low blood pressure
- Low central venous or mixed venous oxygen saturation
- High cardiac index
Organ Dysfunction
- Low oxygen level
- Low urine output
- High creatinine in the blood
- Coagulation (clotting) abnormalities
- Absent bowel sounds
- Low platelets in the blood
- High bilirubin levels
Tissue Perfusion
- High lactate in the blood
- Decreased capillary filling or mottling































